Introduction: Multiple myeloma (MM) is a hematological malignancy characterized by proliferation of abnormal plasma cells in bone marrow. Revised-International Staging System (R-ISS) is generally used as a predictor in newly diagnosed MM (NDMM) since 2015. R-ISS combines ISS with chromosomal abnormalities (CA) and serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). R-ISS I is defined as ISS I without high risk CA and normal LDH, R-ISS III is defined as ISS III with high risk CA or high level LDH, and R-ISS II includes all of the other possible combinations. Therefore, about 60% of NDMM are classified to R-ISS II. However, MM is a highly heterogeneous disease, so the clinical outcome of MM with R-ISS II also must be heterogeneous. Therefore, factors stratifying the majority of MM is needed. C-reactive protein (CRP) is a commonly used inflammatory marker. In particular, highly sensitive (hs) CRP detects lower concentration of CRP as compared with the conventional method, and has been reported to be associated with mortality of lung, breast, and renal cell cancers. In this study, we evaluated the predicting potential of hs-CRP in MM in the novel agent era to see if hs-CRP can develop the stratifying power of R-ISS.
Materials and Methods: The retrospective study examined 80 patients with symptomatic NDMM who had been diagnosed at our institution between April 2006 and September 2019. Patients with infection and/or amyloidosis were excluded. Linkable anonymizing data, including age, gender, immunoglobulin type, symptoms, R-ISS, hs-CRP at diagnosis, time to next treatment (TNT) of the initial treatment, and overall survival (OS) were collected. The concentration of hs-CRP was measured by quantitative latex agglutination turbidimetric immunoassay. The lower detection limit of hs-CRP is 0.01 mg/dL, while that of conventional CRP was 0.10 mg/dL. We analyzed these data using the Kaplan-Meier method, Fisher's exact, multivariate cox proportional hazard models, and log-rank test. P-values ≤0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. This retrospective study was approved by institutional review board in University of Fukui, Japan (No. 20190101).
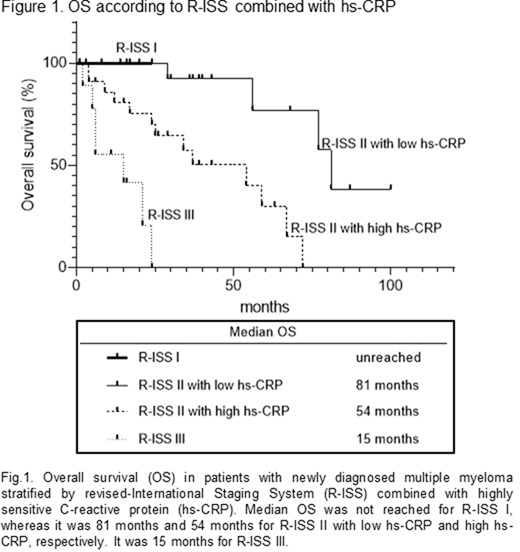
Results: Among 80 patients, 39 (48.8%) were male. Median age at diagnosis was 71 years (range: 36-89 years). IgG, IgA, and BJP types were 56.8%, 25.9%, and 17.3%, respectively. Median follow-up was 29 months (range: 1-120 months). All of the patients were treated with bortezomib and/or lenalidomide-based regimens throughout their clinical courses. R-ISS I, II, and III were 7.3%, 76.4%, and 16.4%, and median OS in patients with R-ISS I, II, and III were unreached, 67, and 15 months, respectively (p<0.0001). Median hs-CRP was 0.10 mg/dL (range: 0.01-8.86 mg/dL), and the patients were divided into 2 groups according to median hs-CRP, consisting of low hs-CRP group (≤0.1 mg/dL, n=42) and high hs-CRP groups (>0.1 mg/dL, n=38). No significant difference in gender, age, immunoglobulin type was observed between 2 groups according to Fisher's exact test. The levels of hs-CRP appeared to be associated with the presence of bone lesions, not hypercalcemia, renal dysfunction, and anemia. There was not significant correlation between hs-CRP and TNT of the initial treatment, due to the variation of the used regimens. However, Kaplan-Meier curves showed that low hs-CRP group had significantly better OS than high hs-CRP group (64 months vs. 54 months, p=0.0116). Multivariate analysis indicated that both R-ISS (hazard ration (HR), 6.19) and hs-CRP (HR, 7.03) were independent prognostic factors for OS. Moreover, comparing the patients with R-ISS II divided by median hs-CRP, OS was significantly longer in R-ISS II with low hs-CRP than R-ISS II with high hs-CRP (median OS: 81 months vs. 54 months, p=0.0009) (Figure 1). Similarly, in the patients with R-ISS III, OS tended to be longer in low hs-CRP group than high hs-CRP group (median OS: 21 months vs. 5.5 months). All the patients with R-ISS I survived within the follow-up period.
Conclusions: Hs-CRP enabled to detect 0.01-0.1 mg/dL, that is not measured by the conventional CRP method. The superiority of hs-CRP contributes to the role as a powerful predictor in MM. The novel staging system that combines hs-CRP and R-ISS may establish better understanding of prognosis in NDMM.
Yamauchi:Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Otsuka: Research Funding; Chugai: Honoraria; Abbie: Research Funding; Solasia Pharma: Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Research Funding; Ono Pharmaceutical: Honoraria; Astellas: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal